Custom Auth Server
Learn how to integrate your auth backend with our in-app wallets solution so you can onboard your users into web3 seamlessly.
This guide will show you how to create your own Auth Server that is compatible with the auth_endpoint strategy. By doing so, you can have full control over user authentication and data security. This allows you to ensure that your application meets specific compliance requirements while also providing a customized sign-in experience.
Navigate to Wallets > In-App Wallets in the thirdweb dashboard.
Create a thirdweb API key if you don't have one or select an existing key to use for this project. Learn more about API keys.

Allowlist domain or bundle IDs in Access Restrictions.
Navigate to the Configuration view and enable Custom Auth Endpoint

Set the Auth Endpoint URL to
https://embedded-wallet.thirdweb.com/api/2023-11-30/embedded-wallet/auth/test-custom-auth-endpointfor testing purposes. You will replace this later with your own auth server endpoint to verify thepayload.- Save the configuration.
- Copy the client ID.
In your preferred thirdweb client SDK, pass the payload you retrieved from logging in to the server.
You can now auth into the wallet and use it to sign transactions like so (see use your own auth for more):
You can set your encryptionKey in either a secret env variable or ask the user to enter a password for it.
** Do not hardcode the encryptionKey in your code. **
A persistent, cross-platform wallet is now created for your user!
Of course, you would use your own auth server instead of the one we provided. The rest of this guide will show you how to create your own auth server.
The following steps will show you how to create a simple auth server that can be used with the embedded wallet.
At a high level, the auth server will:
- Handle login for the user into your application.
- Have a way to get a public identifier for the user.
- Have an endpoint to verify the public identifier and return some basic information about the user
Steps 1 and 2 are up to you to implement. You can use any auth strategy you want.
The endpoint in step 3 is what you register as your auth endpoint on the thirdweb dashboard.
Here's a high-level diagram:
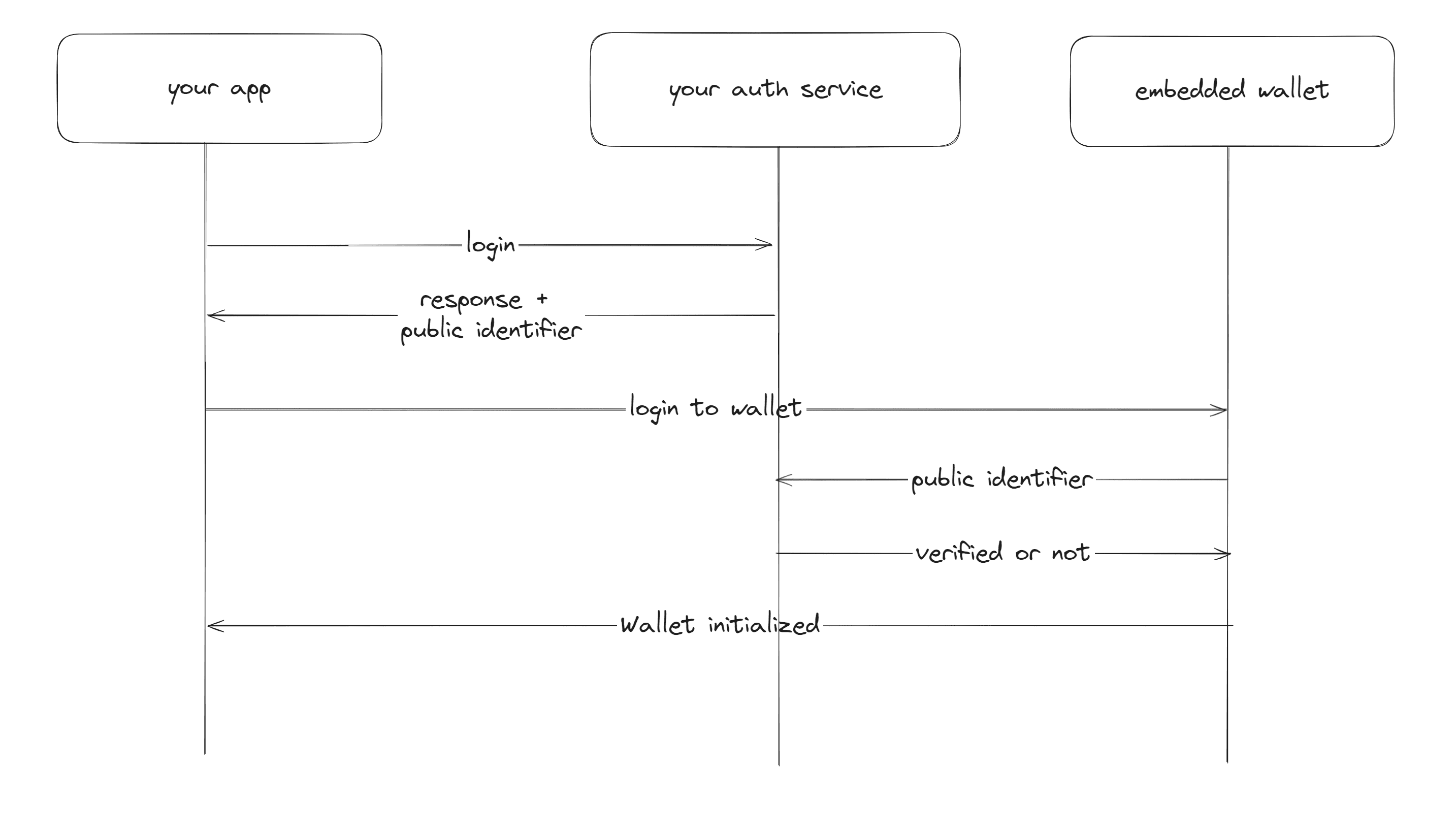
Create a new directory for your project and navigate to it in your CLI
Initialize a new Node.js application
OR
Create the Server:
In the custom-auth-server directory, create a file at the root named server.js and paste the following:
Test Locally
-
Start the server:
-
Test login:
Deploy
To deploy the server, you can use services such as Zeet or Docker.
Integrate In-App Wallets
Refer top the quickstart above to integrate the embedded wallet into your application.